GUI CMS MENU WEB PAGES
SECTION
This menu
system allows the administrative user to enter into all aspects of
the website core and make changes or edit web pages and settings.
Web pages
section.
 |
Edit/View
Existing Pages in Database:
There are
various types of data in this section, all the core data from the
database is viewed in this section and can be edited by selecting the
data to be edited and the editor in which to use. The data can also
be deleted here as well by selecting the data to be deleted and then
clicking on delete.
There are
three editor types to choose from: CSS, HTML, CODE. The CSS option
works only with user web pages and finds the CSS to edit for those
pages. The HTML editor is a WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get)
type editor and it allows the web page HTML code to easily be edited
while seeing how the page will look as its edited and adds the code
into the page for the user. The CODE editor allows any code or text
to be edited to the selected data manually, in some cases as in CSS
this is the only editor that can be used because the HTML editor will
remove any code that the editor sees as invalid.
To
link web pages together as a navigational website, menu items and
links will need to be added in HTML on the pages individually. These
pages and how they are linked can be viewed by clicking on the 'view
website map' upper right of the edit list. Links on the
website map will open the web page for viewing. Links to view user
web pages within the yellow areas of the edit list are in blue. Blue
text within the pink areas are page descriptions and are not links.
Website map:
Website map:
The types
of data in this section are:
The user web
pages in the yellow sections , these can be edited without changing
how the core functions. Pink section is all the core data ranging
from settings to web pages within the core and should be edited
carefully as to not stop the core from functioning properly or
crashing.
Data types:
The data
types are designated by index extensions at the beginning of each
data name. These types are: 'pg' web page data, 'pgd' web pages
description data, 'data' core data, 'sys' system data, 'css' CSS data
for web pages and menus. Some data may not have an extension, that is
unclassified data for the core.
Other
special types are classified within the data name, 'docs' are
documents and 'secure' are secure items such as menus. This section
will have the types described with all the data listed and is color
coded.
The
editors:
There are
two types of editors in this section, HTML and CODE. The HTML editor
adds HTML code for the user and shows how the page will look as it is
edited. The CODE editor is a text editor that any code can be added
to without any changes made to it, unlike the HTML editor which will
remove any invalid code the user may add. Changes do not take effect
until the data is saved.
HTML
Editor
CODE
Editor
Creating
a new database entry:
Database
core items are called 'pages' in WPC and can be thought of as pages
in a book within the database for the core to use, each has a name so
it can be found like a page name and content as the data of that
page. Some pages have attached data such as a page description.
This
section will create the database page for the user with the proper
index extension added to it, or the page can be entered manually by
adding the index extension to the page name. Adding the index
extension will over ride automatic functions and only add a page
'title' or attached data only if its present.
If
the secure page box is checked a secured page will be created and an
attached data page will also be created for that page if there is an
entry in 'page title' at that time. A secured page requires that the
user be logged in to view the page or execute the data. Template data
will no be added to this type page.
If
the system page box is checked the page will be created as system
data for the core to use. No attached data or template data will be
added to this type.
If
no boxes are checked a user web page will be created and a page title
is mandatory along with template selection or the page will not be
created. A list of all available template options will be listed in
the template selection drop down menu. Or it can be left to the
default 'current settings' and the template data currently being used
will be added to the page.
To
link web pages together as a navigational website, menu items and
links will need to be added in HTML on the pages individually. These
pages and how they are linked can be viewed by clicking on the 'view
website map in the web pages section.
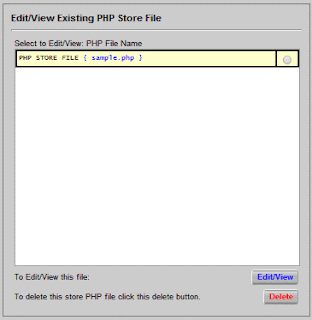
Edit an
existing PHP store file:
Store
files are files the administrative user can create and execute on the
server and use within the website without uploading them in both PHP
and HTML. These files are located at /store/php/ and /store/html/
respectively. They can be opened but this section by the link in blue
and by the directory file list by going to /store/ directly.
To
view the code and edit this PHP file select it from the list and
click 'edit/view'. Or select file to be deleted and click delete.
Creating
a new PHP store file:
Regardless
of whether a PHP extension is added or any other extension the new
file will always have the extension 'php'.
Below
is what the user will see when first the file is created by using the
below to create a new PHP store file.
This
is an explanation of this self inserted code:
<?php
$doc_root=$_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'];
include_once
($doc_root.'/core/system/config/config.php');
// SECURE PAGE BEGIN
//require
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/secure.php');
//if($status !==
"secure") {echo "<a
href='http://".$domain_name."/core/system/admin/login.php'><u>Click
here to login.</u></a>"; exit;}
// SECURE PAGE END
$page=$_GET['page'];
if($page == NULL)
{$page_name="pg.index";}else{$page_name=$page;}
$page_name=str_replace('pg.', 'pg.', $page_name,
$true_pg);
if($true_pg == 0) {$page_name="pg.".$page_name;}
if($options[2]=="template") {$data_name =
$page_name."_".$template;
}else{$data_name = $page_name."_".$options[3];}
$templ_data=$data_name;
// NON-SECURE PAGE BEGIN
str_replace('secure',
'', $data_name, $true);
if($true > 0) {echo
"<p>This is a secure item and can not be displayed here
please <a class='link_b' href='/login'><u>login</u></a>
to see this secure page."; exit;}
// NON-SECURE PAGE END
include
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/db_wpc_core.php');
$page_html=$db_wpc_core_out_decoded;
$data_name="data.x-css";
include
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/db_wpc_core.php');
$page_html=$db_wpc_core_out_decoded.$page_html;
// page HTML data
include
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/templates/'.$template.'/index_html_inc/inc_index_header.php');
echo $page_html;
include
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/templates/'.$template.'/index_html_inc/inc_index_footer.php');
?>
If
the page is not going to use database HTML then delete code not
needed for the page.
For
a secured page un-comment the highlighted code:
// SECURE PAGE BEGIN
//require
($doc_root.'/core/system/includes/secure.php');
//if($status !==
"secure") {echo "<a
href='http://".$domain_name."/core/system/admin/login.php'><u>Click
here to login.</u></a>"; exit;}
// SECURE PAGE END
And
comment out this code highlighted:
// NON-SECURE PAGE BEGIN
str_replace('secure',
'', $data_name, $true);
if($true > 0) {echo
"<p>This is a secure item and can not be displayed here
please <a class='link_b' href='/login'><u>login</u></a>
to see this secure page."; exit;}
// NON-SECURE PAGE
END
IT
IS IMPORTANT TO TAKE NOTE OF PHP STORE FILES THAT MAY CAUSE A
SECURITY BREACH OF THE WEBSITE! MAKE SURE FILES THAT MAY CAUSE THIS
ISSUE ARE UNEXECUTABLE BY USERS NOT LOGGED IN TO THE ADMINISTRATION
AND AUTHORIZED TO HAVE ACCESS TO THE WEBSITE CORE AND DATABASE.
Edit
existing HTML store file:
To
view the code and edit this HTML file select it from the list and
click 'edit/view'. Or select file to be deleted and click delete.
Creating
a new HTML store file:
Regardless
of whether a HTML extension is added or any other extension the new
file will always have the extension 'html'.
Below
is what the user will see when first the file is created.
This
editor will add the inline CSS and HTML for the user as shown below.










No comments:
Post a Comment